Laboratory of Observation
& Research
—
Chemical Interplay
of Science & Art
NeurAstra.xyz is the format in which the fundamental building blocks of matter that constitute our planet bond together through the chemical interplay of science and art.
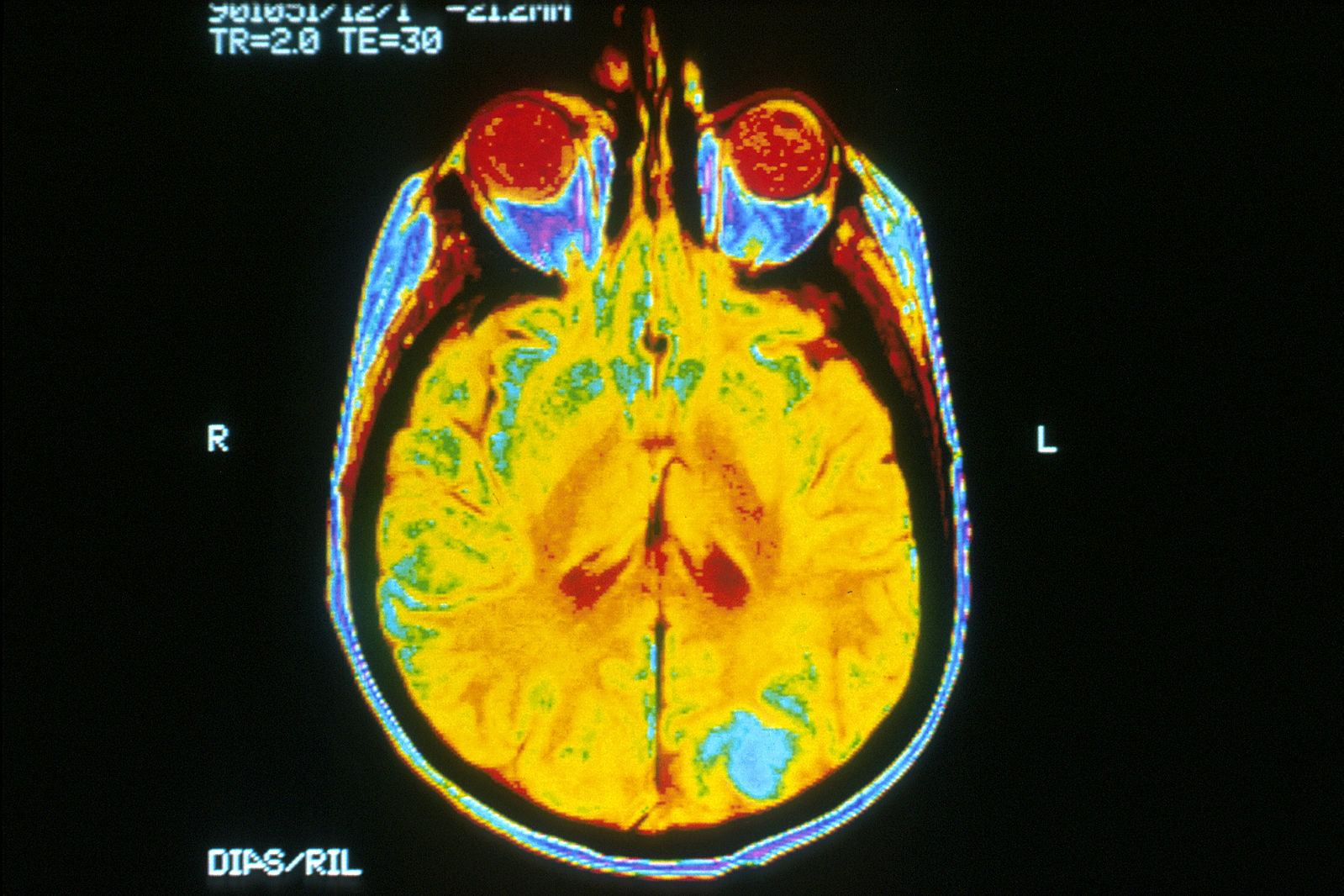
BRAINS
—Imaging Structure & Function
collection: GRAPHIC ESSAYS
areas: neuroscience/design
—
by: NeurAstra
/Les Nouveaux Cosmiques
SYSTEM: (S01) Blue Dot/White Tangerine
—
exhibition: finished
venue: AltaNube 874, Annecy, France
release: 2024
—
—Imaging Structure & Function
collection: GRAPHIC ESSAYS
areas: neuroscience/design
—
by: NeurAstra
/Les Nouveaux Cosmiques
SYSTEM: (S01) Blue Dot/White Tangerine
—
exhibition: finished
venue: AltaNube 874, Annecy, France
release: 2024
—
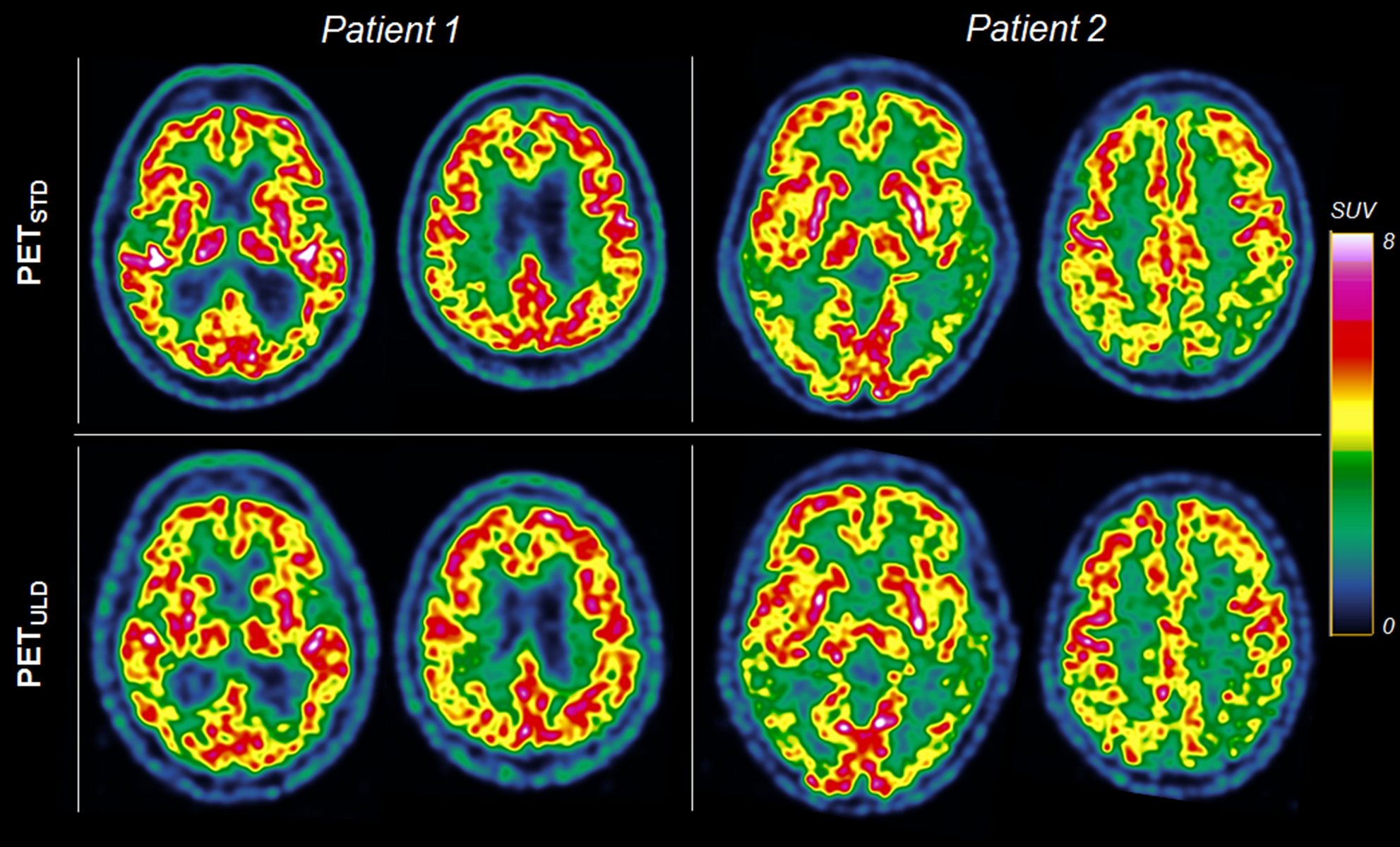
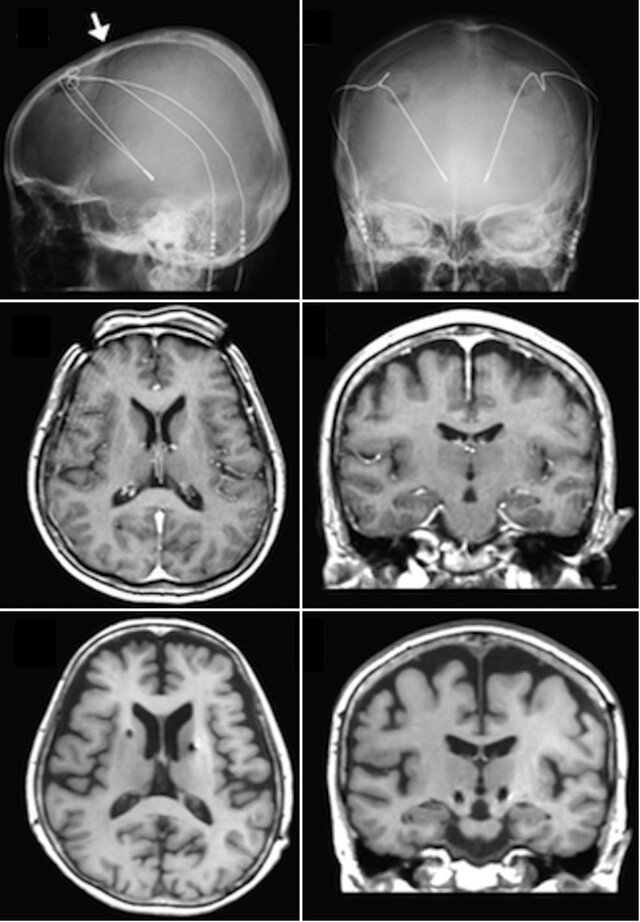
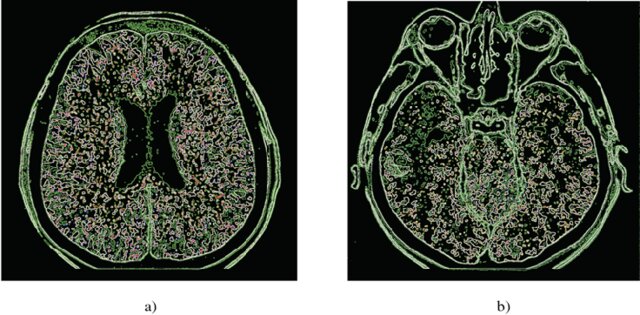
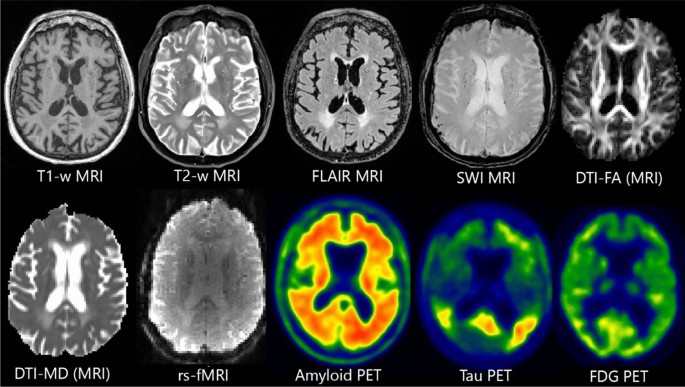
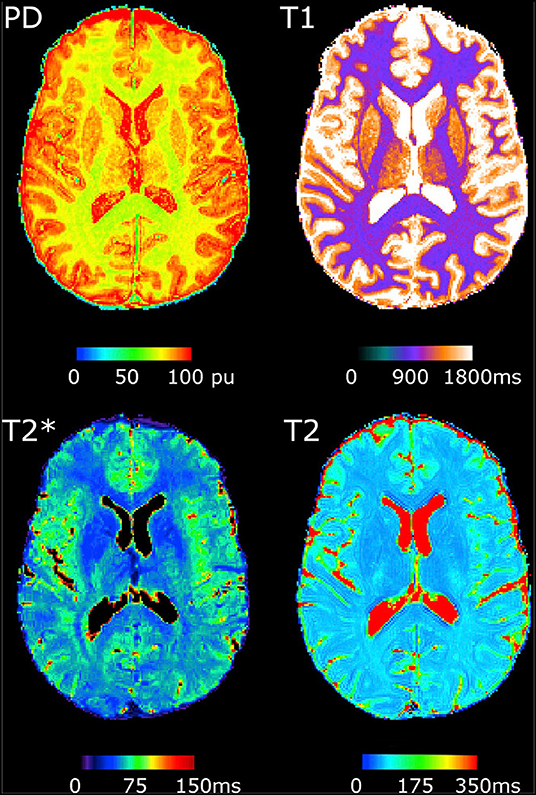
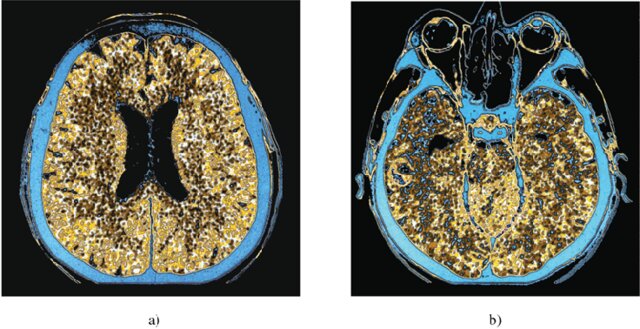
BRAINS retraces the captivating history of neuroimaging—the visualisation of the brain’s structure, function, and biochemical activity—by illustrating the evolution of techniques used to represent the brain over the centuries.
Neuroimaging has significantly advanced from its early beginnings, transforming our ability to diagnose neurological conditions, map brain activity, and guide surgical procedures. From the initial anatomical drawings to today’s high-resolution imaging technologies, the field has made remarkable strides, enabling real-time observation of brain activity and tracking of neural pathways.
Beginning with foundational methods like X-rays and the pioneering use of electroencephalography (EEG), neuroimaging has progressed to sophisticated technologies such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Each technological leap has enhanced our understanding of the brain’s intricate architecture (structure) and its dynamic processes (function), providing deeper insights into the workings of the nervous system.
Neuroimaging has significantly advanced from its early beginnings, transforming our ability to diagnose neurological conditions, map brain activity, and guide surgical procedures. From the initial anatomical drawings to today’s high-resolution imaging technologies, the field has made remarkable strides, enabling real-time observation of brain activity and tracking of neural pathways.
Beginning with foundational methods like X-rays and the pioneering use of electroencephalography (EEG), neuroimaging has progressed to sophisticated technologies such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Each technological leap has enhanced our understanding of the brain’s intricate architecture (structure) and its dynamic processes (function), providing deeper insights into the workings of the nervous system.
OVERVIEW